SaaS Lifecycle Marketing: The 8-Stage Journey

par
Wiktoria Slowikowska
10 oct. 2024
Identifiez et convertissez vos utilisateurs les plus importants
Créer un compte
What is Lifecycle Marketing?
Lifecycle marketing is a holistic approach to customer engagement that focuses on nurturing relationships throughout every stage of the customer journey. Instead of treating all customers the same, lifecycle marketing recognizes that customers have different needs and behaviors depending on where they are in their relationship with your brand.
This strategy aims to provide the right message, to the right person, at the right time, maximizing customer satisfaction, retention, and ultimately, lifetime value. It's about creating a seamless, personalized experience that keeps customers engaged from their first interaction with your brand through to becoming loyal advocates.
Creating a Customer Lifecycle Marketing Strategy
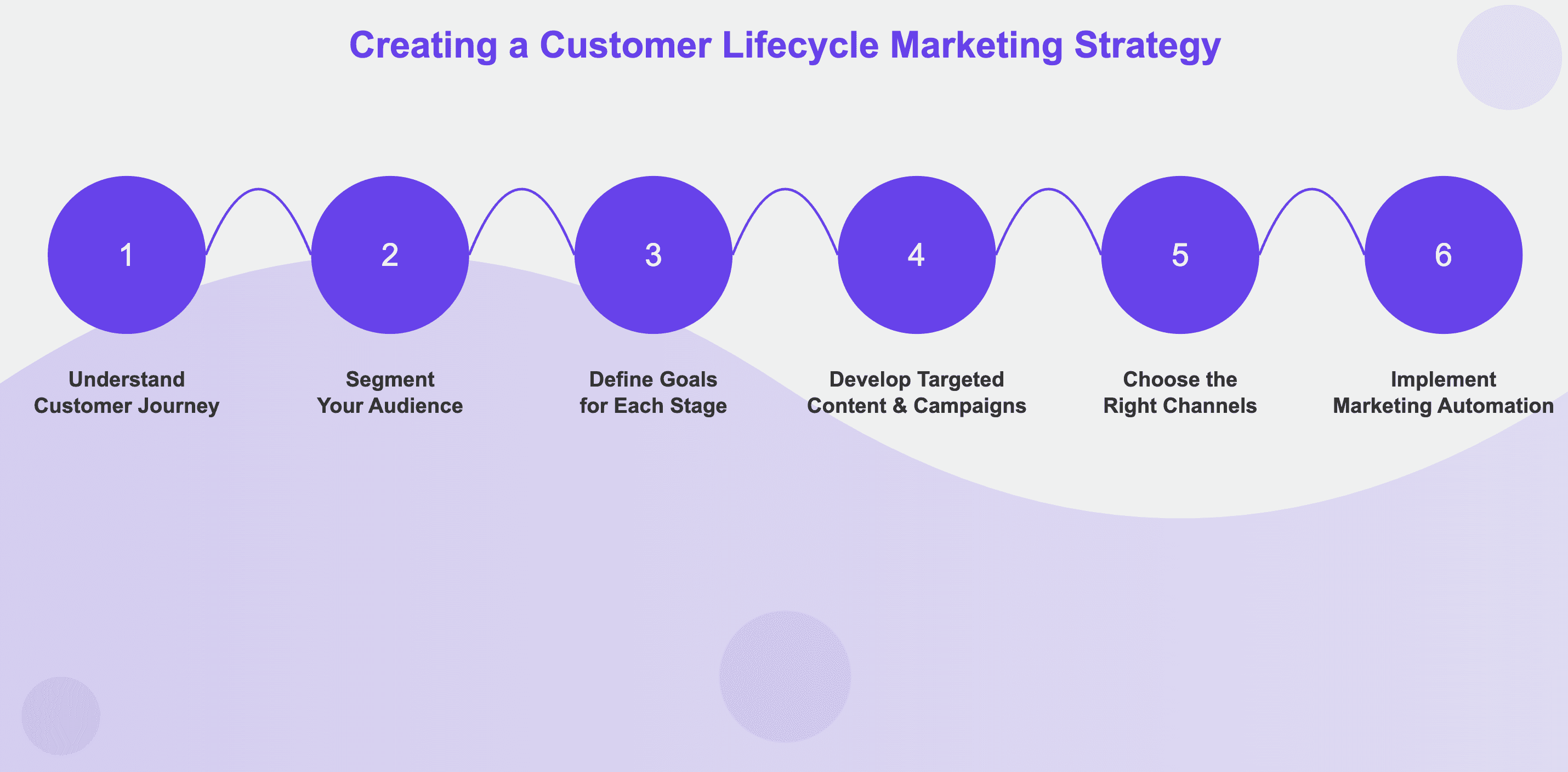
Developing an effective lifecycle marketing strategy involves several key steps:
Understand Your Customer Journey
Map out every touchpoint a customer has with your brand, from initial awareness to post-purchase interactions. How to do it: List all ways customers interact with your brand - from discovering your product to using it long-term. Include online (website visits, emails) and offline (phone calls, events) touchpoints. Create a visual flowchart or timeline. Consult with sales, support, and product teams to ensure you're not missing any key interactions.Segment Your Audience
Divide your customers into groups based on their behaviors, preferences, and stage in the lifecycle. How to do it: Analyze your customer data to identify patterns. Group customers by factors like product usage, industry, company size, or tenure. Use your CRM or analytics tools to help. Create segments like "New sign-ups," "Power users," or "At-risk accounts." Keep these segments flexible as you learn more about your customers.Define Goals for Each Stage
Determine what you want to achieve at each stage of the lifecycle. How to do it: For each stage, define specific, measurable objectives. For example, in the awareness stage, aim to increase website visits. For retention, focus on reducing churn rate. Set clear targets like "Increase trial sign-ups by 20% this quarter" or "Reduce churn from 5% to 3% in six months." Use these goals to guide your strategies and measure success.Develop Targeted Content and Campaigns
Create messaging and offers tailored to each segment and lifecycle stage. How to do it: Address the specific needs and questions of each segment at every stage. For new users, create 'getting started' guides. For long-term customers, develop advanced tips or exclusive content. Plan your campaigns using a content calendar, including various formats like blog posts, emails, and in-app messages. Always align your content with the goals for each stage.Choose the Right Channels
Identify the most effective communication channels for each stage and segment. How to do it: Consider where your customers spend time and how they prefer to receive information. Use data to see which channels perform well. Create a matrix matching customer segments and lifecycle stages with appropriate channels. For B2B SaaS, LinkedIn might work for awareness, while email could be better for engaging existing customers. Aim for a consistent multi-channel approach.Implement Marketing Automation
Use tools to deliver personalized experiences at scale. How to do it: Select a marketing automation platform that integrates with your CRM. Set up automated email sequences for different segments and stages, like welcome series or re-engagement campaigns. Use customer data to trigger campaigns based on behaviors or milestones. Test different messages and timing. Remember, automation should enhance personalization, not replace human touch entirely.
Now, let's dive into each stage of the customer lifecycle, explaining what happens, what businesses should do, and how to implement effective strategies.
The Stages of Lifecycle Marketing
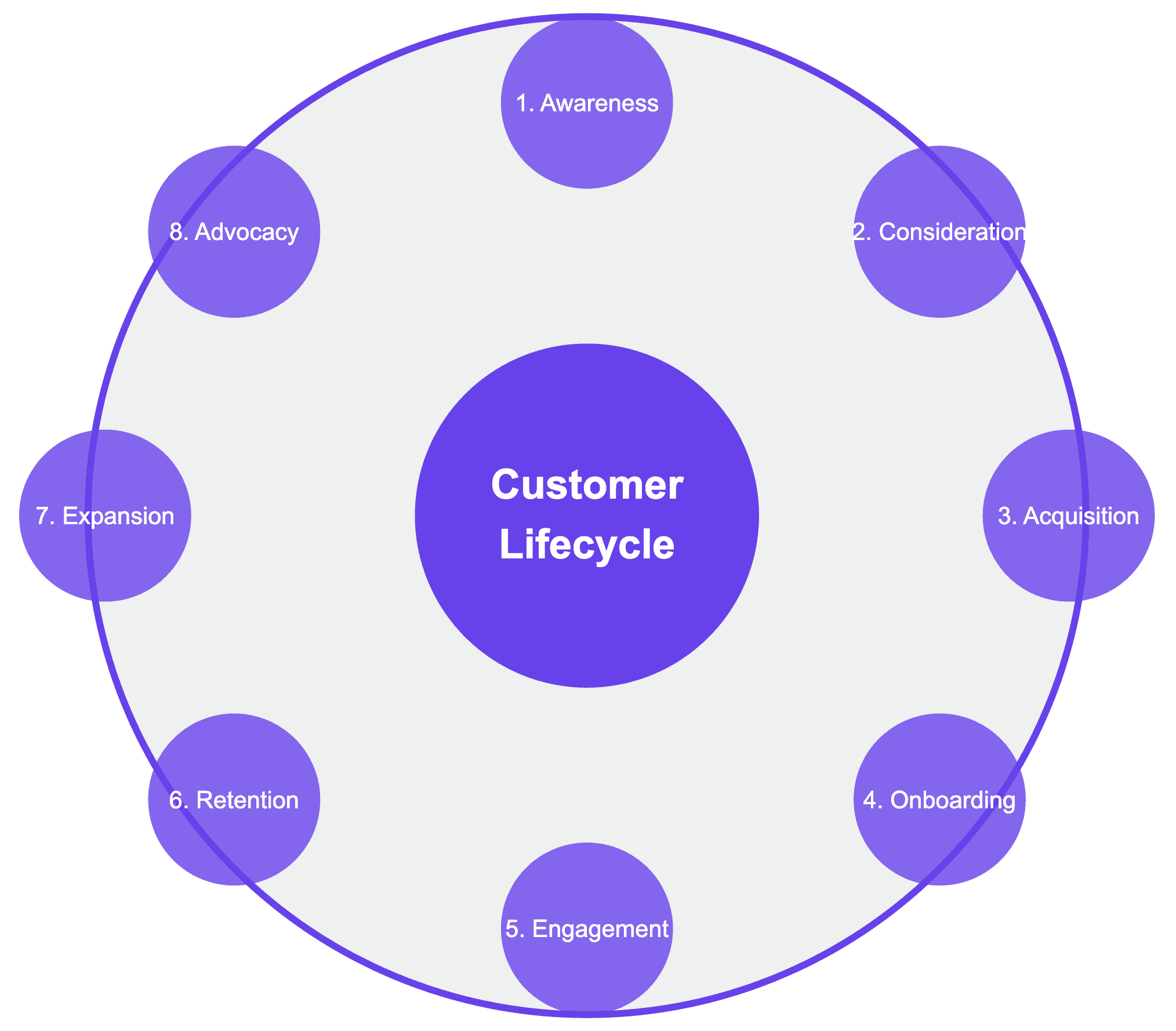
1. Awareness
What It Is: This is when potential customers first become aware of your brand or product. They might be searching for solutions to a problem or simply stumbling upon your content.
What to Do:
Create valuable, informative content that addresses your target audience's pain points.
Increase your brand's visibility through various marketing channels.
How to Implement:
Develop a content marketing strategy focusing on SEO-optimized blog posts, videos, and infographics.
Create a free tool that solves a small part of the problem your SaaS addresses.
Leverage social media platforms to share your content and engage with potential customers.
Use targeted advertising to reach your ideal audience.
Participate in industry events or webinars to increase brand visibility.
2. Consideration
What It Is: Prospects are actively evaluating your product or service alongside competitors.
What to Do:
Provide detailed information about your offerings.
Differentiate yourself from competitors.
Address potential objections or concerns.
How to Implement:
Create comparison guides or feature matrices showcasing your unique selling points.
Offer free trials, demos, or consultations to let prospects experience your product.
Develop case studies and testimonials to build trust and credibility.
Use retargeting ads to stay top-of-mind with interested prospects.
3. Acquisition
What It Is: The prospect decides to become a customer, making their first purchase or signing up for your service.
What to Do:
Make the purchase process as smooth as possible.
Reinforce the customer's decision to choose your brand.
How to Implement:
Optimize your checkout process to reduce friction.
Send a welcome email series introducing your product and setting expectations.
Provide clear next steps or quick start guides to help customers get immediate value.
Offer a satisfaction guarantee or easy return policy to reduce perceived risk.
4. Onboarding
What It Is: The crucial period where new customers start using your product or service.
What to Do:
Help customers quickly realize value from your product.
Provide necessary education and support.
How to Implement:
Create interactive product tours or video tutorials.
Set up a series of onboarding emails guiding users through key features.
Offer personalized onboarding sessions for high-value customers.
Use in-app messaging to provide contextual help and feature discovery.
5. Engagement
What It Is: Customers are actively using your product and integrating it into their routines.
What to Do:
Encourage regular usage of your product.
Continuously demonstrate value.
Gather feedback for improvement.
How to Implement:
Send regular usage reports highlighting the benefits they're receiving.
Create a content hub with tips, best practices, and advanced usage guides.
Implement a customer feedback loop with surveys and feature request options.
Use gamification elements to incentivize desired behaviors.
6. Retention
What It Is: Keeping customers satisfied and subscribed over the long term.
What to Do:
Proactively address potential issues or dissatisfaction.
Continuously add value to the customer relationship.
How to Implement:
Develop a proactive customer success program to identify and assist at-risk customers.
Offer exclusive content, features, or events to loyal customers.
Implement a loyalty program rewarding long-term customers.
Regularly communicate product updates and improvements.
7. Expansion
What It Is: Encouraging customers to increase their engagement, perhaps by upgrading their plan or purchasing additional products.
What to Do:
Identify opportunities for upselling or cross-selling.
Demonstrate the added value of higher-tier offerings.
How to Implement:
Use customer data to suggest relevant upgrades or complementary products.
Create clear, value-driven upgrade paths.
Offer exclusive features or priority support to higher-tier customers.
Provide bundle deals or special upgrade offers at strategic times.
8. Advocacy
What It Is: Turning satisfied customers into brand advocates who recommend your product to others.
What to Do:
Identify and nurture potential advocates.
Make it easy and rewarding for customers to spread the word.
How to Implement:
Develop a referral program with meaningful incentives.
Create shareable content that customers can easily pass along to their networks.
Highlight customer success stories and testimonials in your marketing.
Engage with and amplify positive customer feedback on social media.
Conclusion
Lifecycle marketing is a powerful approach that recognizes the evolving nature of customer relationships. By tailoring your marketing efforts to each stage of the customer journey, you can create more meaningful interactions, improve customer satisfaction, and drive long-term business growth.
Remember, the key to successful lifecycle marketing is personalization, continuous value delivery, and adaptability. Regularly analyze your data, listen to customer feedback, and be prepared to adjust your strategies as needed. With a well-executed lifecycle marketing approach, you can build a loyal customer base that not only continues to choose your brand but actively promotes it to others.




