The Modern SaaS Customer Journey: From Awareness to Advocacy

by
Aleksa Mitrović
Oct 7, 2024
Identify and convert your most valuable users
Sign Up
SaaS companies face the challenge of not just acquiring customers, but nurturing them through a complex journey from initial awareness to long-term advocacy. Understanding and optimizing this journey is crucial for sustainable growth and success in the competitive SaaS market.
This blog post delves into the intricacies of the modern SaaS customer journey, exploring its key stages, the role of data and personalization, and strategies for optimization.
The Evolution of the SaaS Customer Lifecycle
The SaaS customer lifecycle has undergone significant transformation in recent years. As the market has matured and competition has intensified, companies have had to shift their focus from simple acquisition to a more holistic view of the customer journey. This evolution reflects a deeper understanding of the long-term value of customer relationships and the importance of customer success in driving sustainable growth.
In the early days of SaaS, companies often focused primarily on acquiring new customers and driving initial adoption. However, it quickly became apparent that this approach was not sustainable. High customer churn rates and the realization that it's far more cost-effective to retain existing customers than to acquire new ones led to a shift in strategy.
Today, the SaaS customer lifecycle is viewed as a continuous process of engagement, value delivery, and relationship building. This new paradigm recognizes that every interaction a customer has with a SaaS product or company is an opportunity to strengthen the relationship and drive long-term success.
Key Stages in the Modern SaaS Customer Journey

The modern SaaS customer journey can be broken down into two interconnected frameworks: the buying stages and the funnel stages. Understanding both is crucial for SaaS companies looking to optimize their customer experience and drive growth.
The Buying Stages
Awareness: This is where potential customers first become aware of your SaaS product and the problem it solves. At this stage, marketing efforts such as content marketing, social media engagement, and targeted advertising play a crucial role in capturing attention and generating interest.
Consideration: During this stage, potential customers evaluate your product against competitors. They scrutinize features, pricing, and reviews to determine if your solution meets their needs. Providing detailed product information, comparison guides, and case studies can be particularly effective at this stage.
Purchase: The customer decides to buy your SaaS product. This stage involves the actual transaction and any initial setup required. Ensuring a smooth, frictionless purchase process is key to preventing last-minute drop-offs.
Adoption: After purchasing, the customer starts using your product. Effective onboarding is crucial here to ensure they understand how to use the product and quickly see its value. This might involve guided tours, tutorial videos, or personalized onboarding sessions.
Retention: Keeping customers engaged and satisfied is an ongoing process. This involves providing excellent customer support, regular product updates, and possibly loyalty programs. Proactive communication about new features or use cases can help maintain engagement.
Advocacy: Satisfied customers become advocates for your product, recommending it to others and providing testimonials or reviews. Encouraging and facilitating this advocacy can significantly boost your marketing efforts and credibility.
The Funnel Stages
Visitors: These are individuals who visit your website or app but haven't yet registered. The goal at this stage is to provide compelling information that encourages them to take the next step.
Free Users: These are users who have registered for a free account, allowing them to explore your product and determine if it meets their needs. Providing a great free experience while showcasing the value of premium features is key.
Trial Users (Optional): If you offer a trial period, this stage allows users to test premium features before committing to a paid plan. It's crucial to demonstrate clear value during this period to drive conversions.
Paid Users: These are customers who have converted to a paid plan, accessing all premium features. The focus here is on ensuring they're getting maximum value from the product to encourage retention and potential upgrades.
Churned or Brand Ambassadors: The final stage represents two possible outcomes. Users either churn (cancel their subscription) or become brand ambassadors who actively promote your product. Understanding the factors that lead to each outcome is crucial for optimizing your customer journey.
The Role of Data and Personalization in Mapping Customer Journeys
In today's competitive SaaS landscape, a one-size-fits-all approach to the customer journey is no longer sufficient. Data-driven personalization has become a critical factor in creating engaging, effective customer experiences at every stage of the journey.
The key to successful personalization lies in leveraging user data to tailor the experience to each individual's needs, preferences, and behaviors. This involves collecting and analyzing data from various touchpoints throughout the customer journey, including:
Demographic information
Usage patterns
Customer support interactions
Feedback and survey responses
By harnessing this data, SaaS companies can create highly personalized experiences that speak directly to each user's unique situation. For example:
Contextual onboarding: Tailoring the onboarding process based on the user's role, industry, or specific use case.
Personalized feature recommendations: Suggesting relevant features or use cases based on the user's behavior and similar users' experiences.
Targeted communication: Sending customized emails or in-app messages that address the user's specific needs or challenges.
Adaptive user interfaces: Adjusting the UI to highlight features that are most relevant to the individual user.
It's important to note that personalization should extend across the entire customer journey, from initial awareness through to long-term retention and advocacy. By consistently delivering relevant, personalized experiences, SaaS companies can significantly improve engagement, satisfaction, and ultimately, customer lifetime value.
Strategies for Optimizing Critical Touchpoints
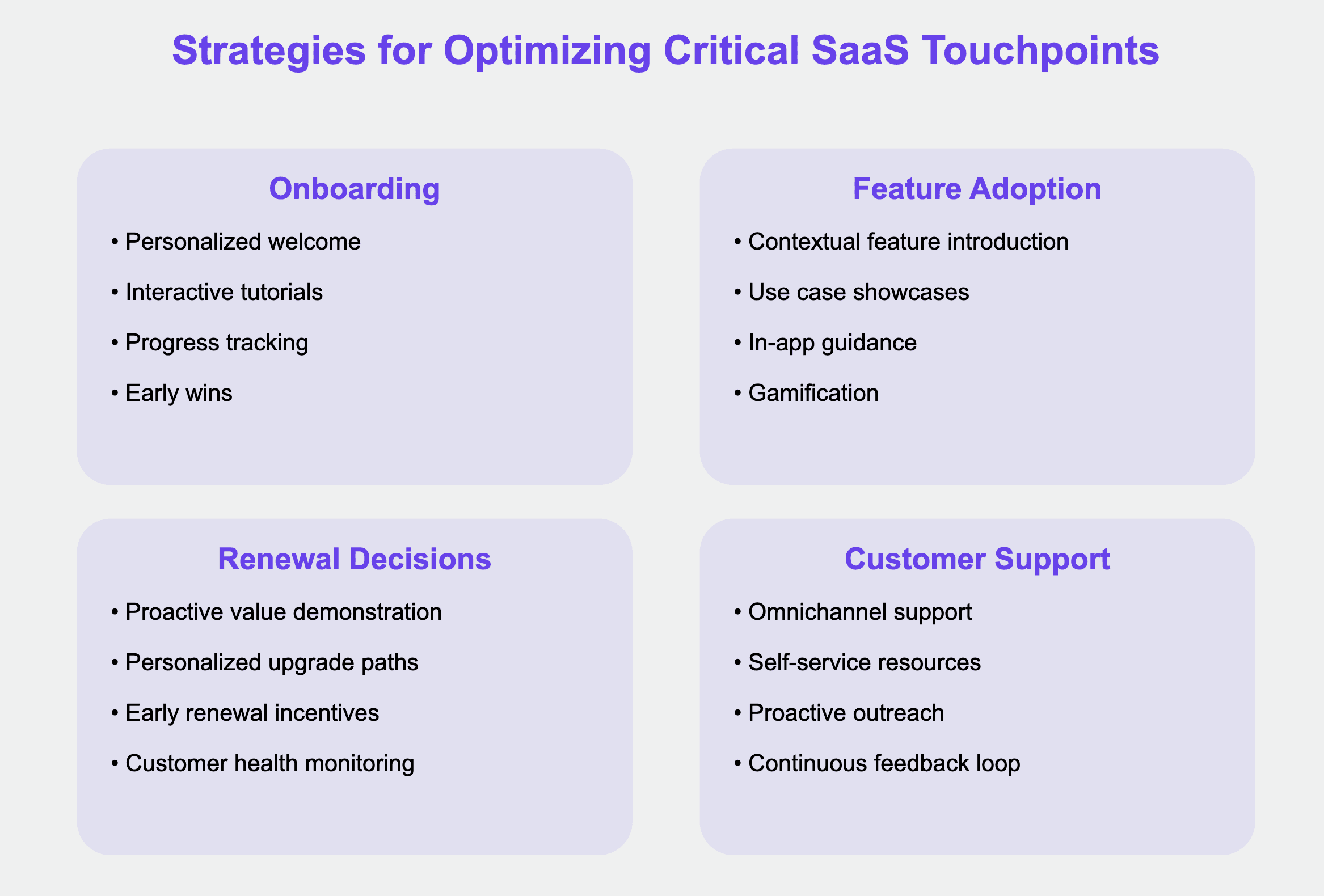
To maximize the effectiveness of your SaaS customer journey, it's essential to focus on optimizing key touchpoints. Here are some strategies for crucial stages:
Onboarding
Personalized welcome: Create a tailored onboarding experience based on the user's role, industry, or stated goals.
Interactive tutorials: Develop engaging, hands-on tutorials that guide users through key features.
Progress tracking: Implement a clear onboarding checklist or progress bar to motivate users to complete setup.
Early wins: Design the onboarding process to deliver quick wins, demonstrating value as soon as possible.
Feature Adoption
Contextual feature introduction: Introduce new features at relevant moments based on the user's behavior.
Use case showcases: Highlight real-world examples of how other users are benefiting from specific features.
In-app guidance: Provide tooltips or walkthroughs for complex features to reduce friction.
Gamification: Implement challenges or rewards for trying new features to encourage exploration.
Renewal Decisions
Proactive value demonstration: Before renewal, proactively showcase the value the customer has received (e.g., time saved, ROI achieved).
Personalized upgrade paths: Offer tailored upgrade options based on the user's current usage and potential needs.
Early renewal incentives: Provide benefits for early renewal to reduce last-minute churn.
Customer health monitoring: Implement a system to identify at-risk customers and intervene before renewal time.
Customer Support
Omnichannel support: Offer support across multiple channels (e.g., chat, email, phone) to cater to different preferences.
Self-service resources: Develop a comprehensive knowledge base and community forum to empower users to find answers independently.
Proactive outreach: Use data to identify potential issues and reach out to users before they encounter problems.
Continuous feedback loop: Regularly collect and act on customer feedback to improve the product and support experience.
Measuring Success in the SaaS Customer Journey
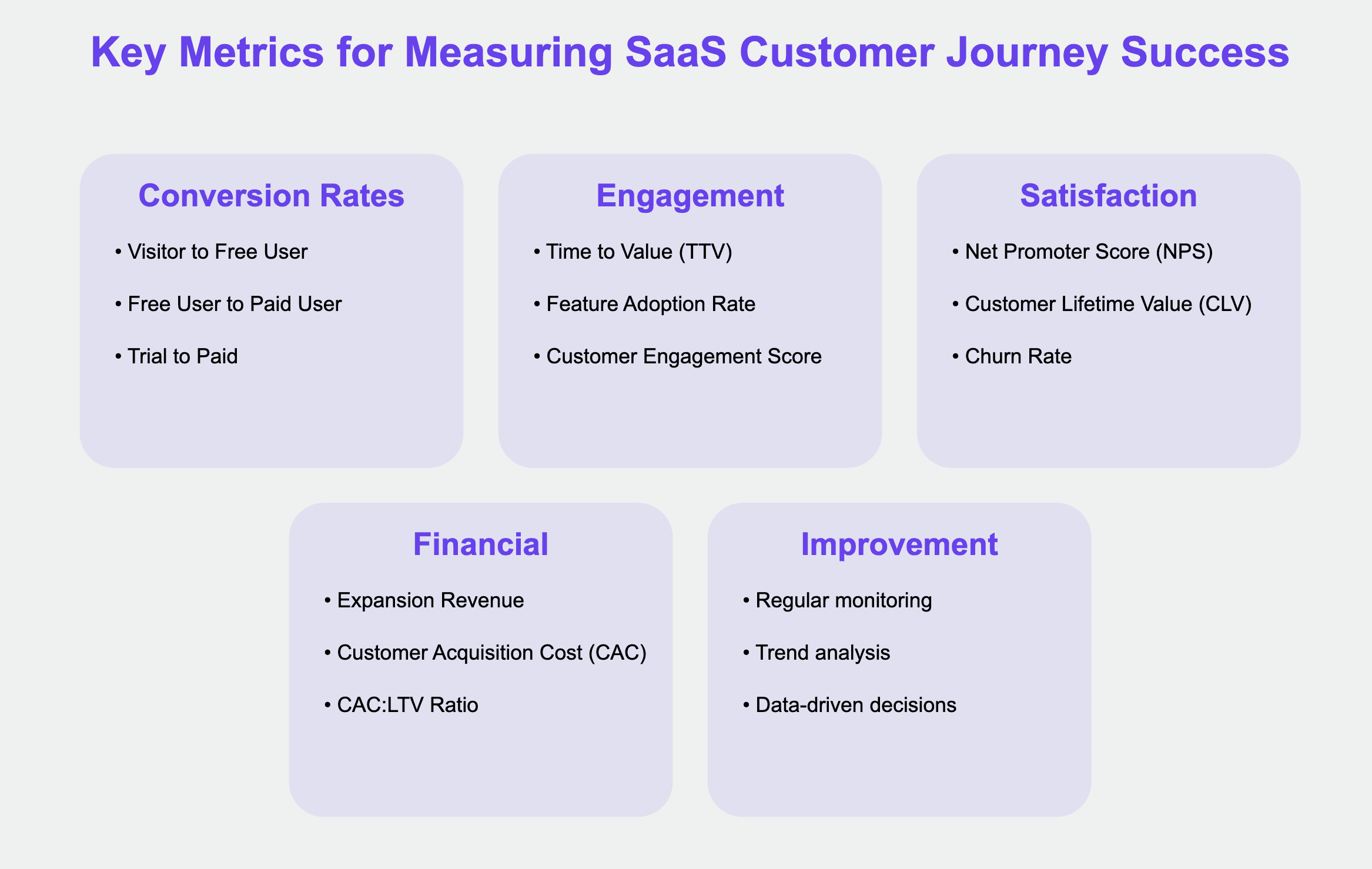
To ensure the effectiveness of your customer journey strategies and drive continuous improvement, it's crucial to track key metrics and KPIs. Here are some essential metrics to consider:
Conversion Rates Between Stages:
Visitor to Free User conversion rate
Free User to Paid User conversion rate
Trial to Paid conversion rate (if applicable)
Time to Value (TTV): How quickly users are able to achieve their first meaningful outcome with your product.
Feature Adoption Rate: The percentage of users who adopt key features within a specific timeframe.
Customer Engagement Score: A composite metric that takes into account factors like login frequency, feature usage, and interaction with support/community.
Net Promoter Score (NPS): A measure of customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): The total revenue you can expect from a customer over the course of your relationship.
Churn Rate: The percentage of customers who cancel their subscription within a given period.
Expansion Revenue: Additional revenue generated from existing customers through upsells or cross-sells.
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): The total cost of acquiring a new customer.
CAC:LTV Ratio: The ratio between Customer Acquisition Cost and Customer Lifetime Value, indicating the efficiency of your growth strategy.
By regularly monitoring these metrics and analyzing trends over time, you can identify areas for improvement in your customer journey and make data-driven decisions to optimize the experience.
Conclusion
The SaaS customer journey has evolved into a complex, multifaceted process that extends far beyond the initial sale. By understanding the key stages of this journey, leveraging data for personalization, optimizing critical touchpoints, and consistently measuring success, SaaS companies can create a customer experience that drives long-term growth and success.
Remember, the most successful SaaS companies view the customer journey not as a linear path, but as an ongoing cycle of engagement and value delivery. By continuously refining and optimizing this journey based on data and customer feedback, you can build stronger relationships with your users, reduce churn, and ultimately drive sustainable growth in the competitive SaaS landscape.




