Lifecycle Marketing SaaS: A Guide to Customer Success

by
Wiktoria Slowikowska
Sep 26, 2024
Identify and convert your most valuable users
Sign Up
This guide will help you transform your approach to customer relationships and drive long-term success. Let's explore the key strategies and concepts that will elevate your SaaS marketing game.
Understanding Lifecycle Marketing in SaaS
Lifecycle marketing in SaaS is about nurturing customer relationships from initial contact through to long-term loyalty. It recognizes the ongoing nature of SaaS products and aims to provide value at every stage of the customer journey. This approach is crucial in the SaaS world, where customer retention is as important as acquisition.
Why It's Different from Traditional Marketing
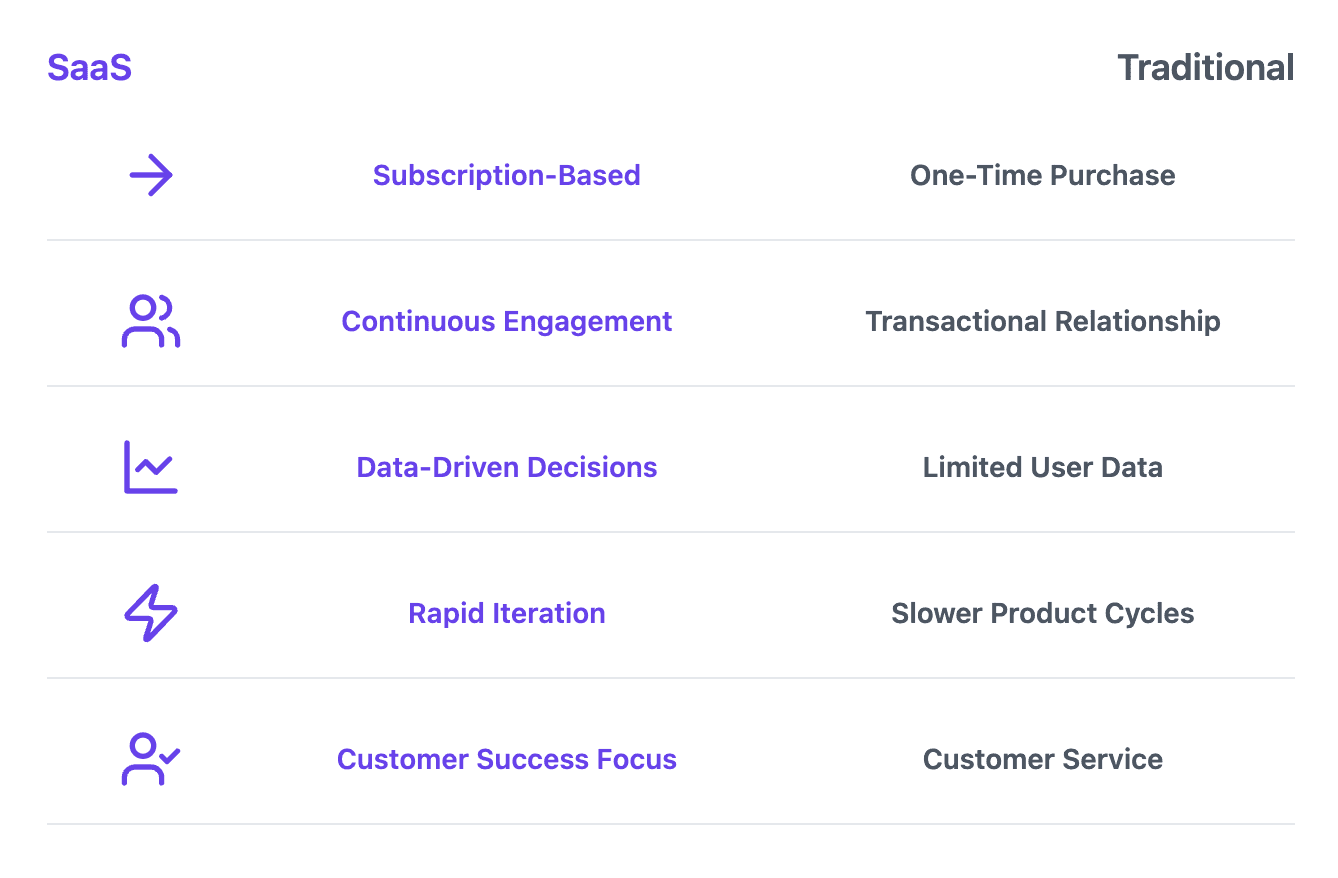
SaaS marketing differs from traditional approaches in several key ways:
Subscription-Based Model: Unlike one-time purchases, SaaS focuses on ongoing subscriptions. This means the relationship with the customer extends far beyond the initial sale.
Continuous Engagement: Success in SaaS requires keeping users actively engaged over time. It's not just about making a sale, but ensuring the customer continues to find value in the product.
Data-Driven Decisions: SaaS companies have access to rich user data, allowing for highly targeted and personalized marketing strategies. This data can inform everything from product development to customer communication.
Rapid Iteration: SaaS products can be updated quickly, allowing for continuous improvement based on user feedback. This agility is a key advantage in the fast-paced tech world.
Customer Success Focus: Many SaaS companies have dedicated customer success teams to ensure users achieve their goals with the product. This proactive approach to customer satisfaction is a hallmark of SaaS marketing.
The SaaS Customer Lifecycle: Stages and Strategies
Understanding the customer lifecycle is crucial for effective marketing. Let's break down each stage and explore strategies for success.
1. Acquisition: Attracting Potential Customers
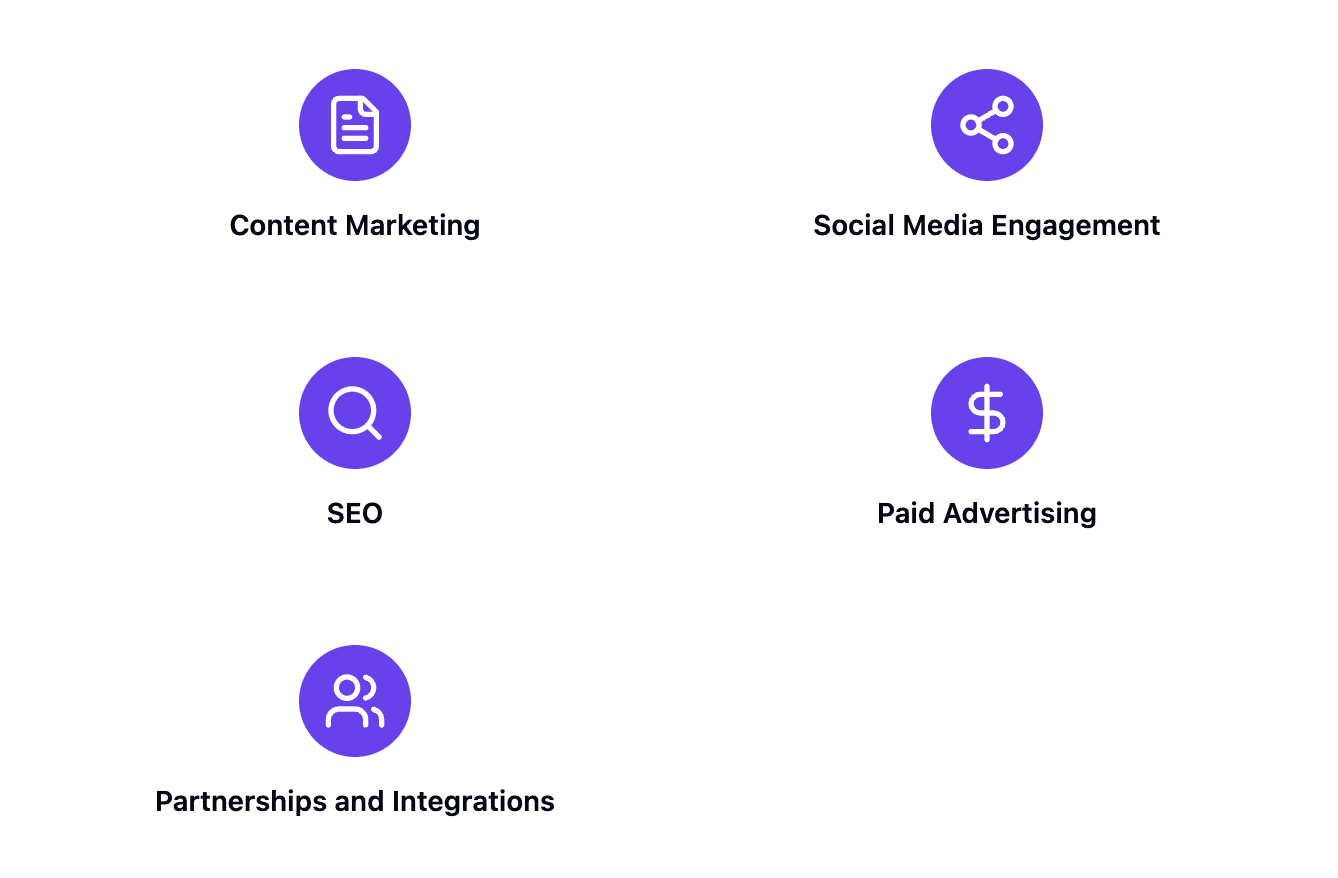
The journey begins with acquisition – catching the attention of potential users and drawing them into your ecosystem. Successful acquisition strategies often include:
Content Marketing: Create valuable, problem-solving content that addresses your target audience's needs. This could include blog posts, whitepapers, webinars, and podcasts.
Social Media Engagement: Build a presence on platforms where your potential customers spend time. Share industry insights, participate in relevant conversations, and showcase your product's benefits.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Ensure your product is discoverable when potential customers are searching for solutions. This includes optimizing your website content, building quality backlinks, and focusing on relevant keywords.
Paid Advertising: Utilize platforms like Google Ads, LinkedIn Ads, or Facebook Ads to reach your target audience directly. Tailor your ads to specific segments for better results.
Partnerships and Integrations: Collaborate with complementary products or services to expand your reach and provide added value to potential customers.
Example: Dropbox mastered acquisition through its referral program, offering extra storage space for referrals. This incentivized users to spread the word, leading to exponential growth. At its peak, this program was bringing in 35% of Dropbox's daily new signups.
2. Onboarding: Setting the Stage for Success
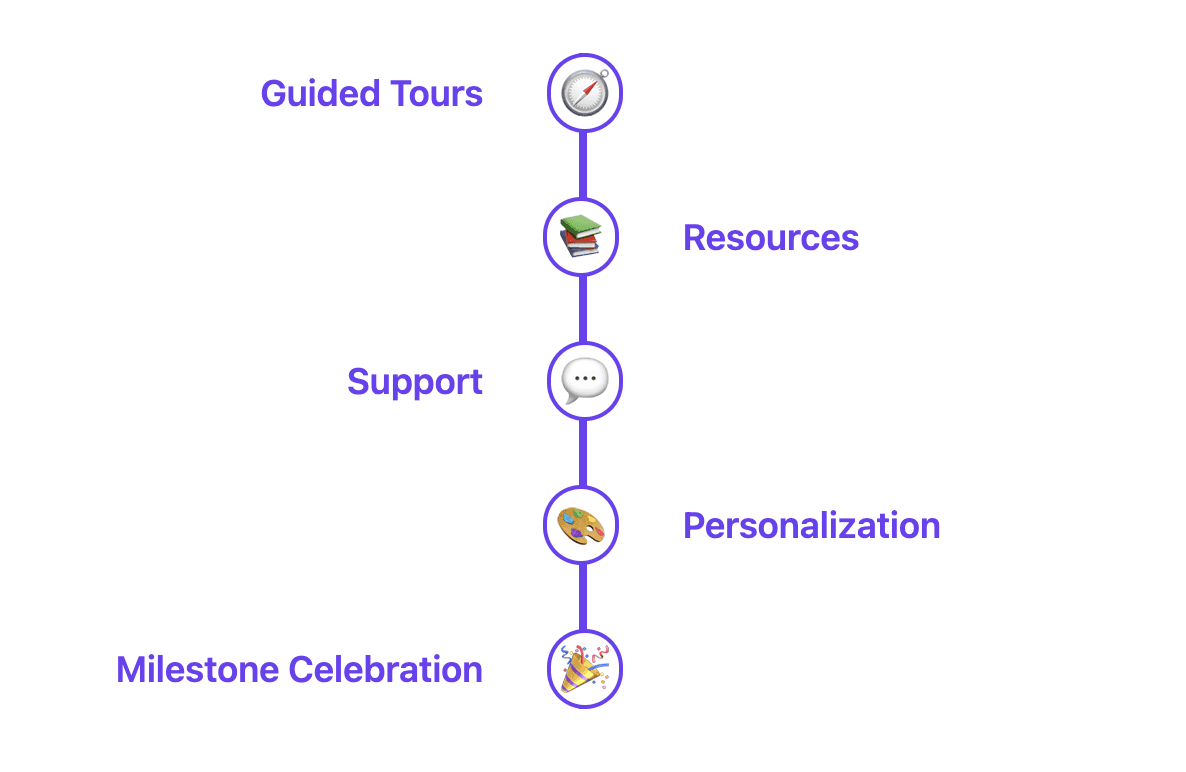
Once a user signs up, the onboarding process becomes critical. This stage can make or break the customer relationship. Effective onboarding typically involves:
Guided Product Tours: Show users how to navigate and use key features. This could be through interactive walkthroughs or video tutorials.
Tutorials and Resources: Provide easy access to learning materials, such as knowledge bases, FAQs, and getting started guides.
Responsive Support: Ensure help is readily available when users need it, through channels like live chat, email support, or phone assistance.
Personalized Onboarding: Tailor the onboarding experience based on the user's role, goals, or industry. This personalization can significantly improve user adoption rates.
Milestone Celebrations: Acknowledge and celebrate user progress as they set up and start using the product. This positive reinforcement can boost engagement.
Example: Slack excels at onboarding new users. When you first join a Slack workspace, you're greeted by Slackbot, an automated assistant that guides you through the basic features. It prompts you to set up your profile, explains how channels work, and even encourages you to send your first message. This interactive approach makes the onboarding process engaging and helps users quickly understand the platform's value.
3. Engagement: Fostering Active Usage
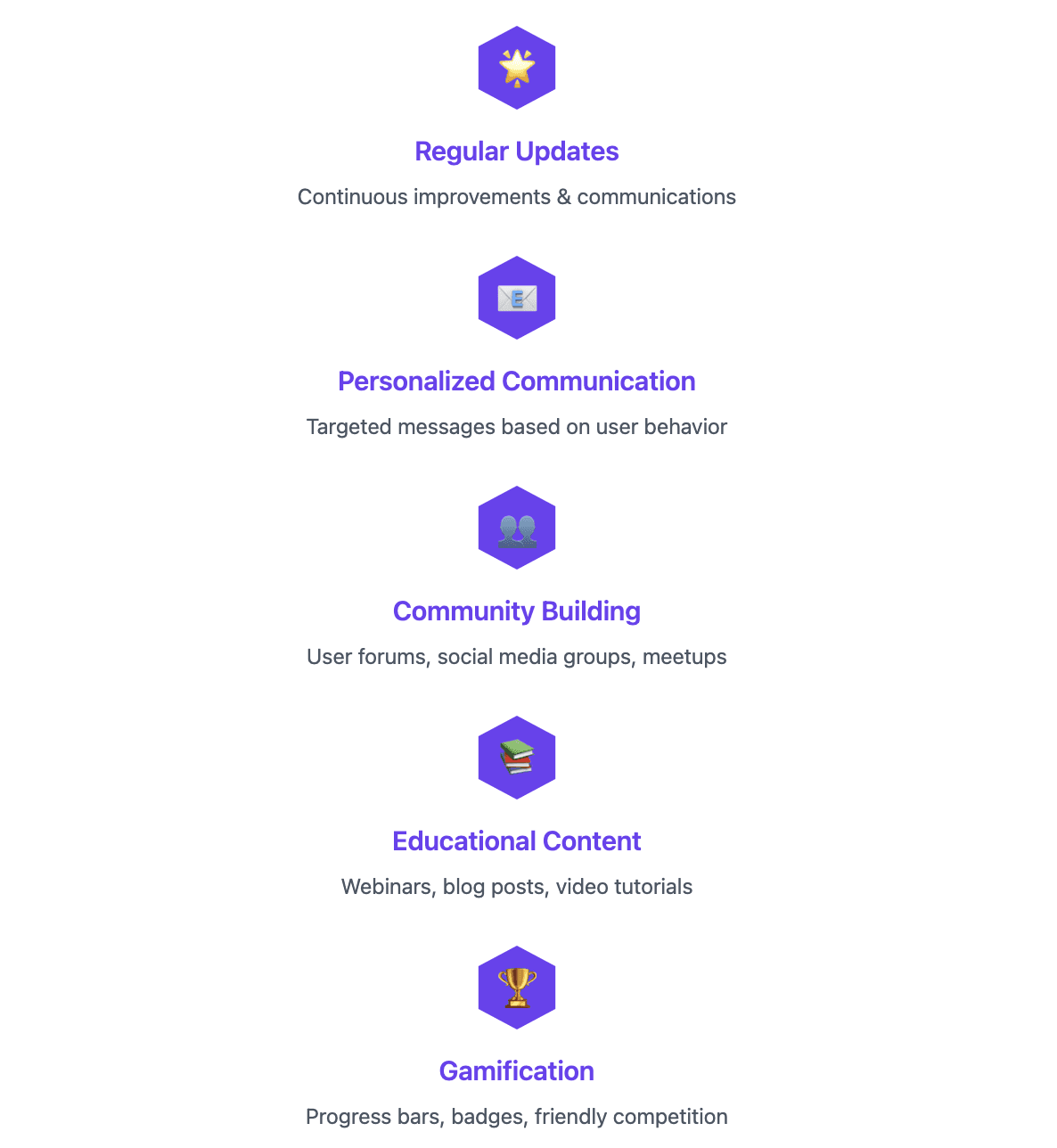
Keeping users engaged is the next challenge. This stage is all about demonstrating ongoing value and encouraging regular product use. Strategies include:
Regular Updates and New Features: Continuously improve the product and communicate these improvements to users. This could involve release notes, product update emails, or in-app notifications.
Personalized Communication: Send targeted emails or in-app messages based on user behavior and preferences. For example, suggest features they haven't used yet that could be beneficial.
Community Building: Create spaces for users to connect, share experiences, and learn from each other. This might include user forums, social media groups, or local meetups.
Educational Content: Provide ongoing education about your product and industry through webinars, blog posts, or video tutorials. This helps users get more value from your product and positions you as an industry leader.
Gamification: Incorporate game-like elements to encourage regular usage and feature adoption. This could include progress bars, achievement badges, or friendly competition among users.
Example: Grammarly keeps users engaged through regular, personalized emails. They send weekly writing stats, showing how many words you've checked, how many mistakes you've corrected, and how your performance compares to other Grammarly users. This gamification aspect encourages regular use of the product and demonstrates its ongoing value to users.
4. Retention: Building Long-Term Loyalty

The ultimate goal is to turn users into long-term, loyal customers. Retention strategies often focus on:
Proactive Customer Success: Anticipate and address customer needs before they become issues. This might involve regular check-ins, usage analysis, and personalized recommendations.
Loyalty Programs: Reward long-term customers with exclusive benefits or discounts. This could include early access to new features, premium support, or usage-based rewards.
Continuous Value Demonstration: Regularly show customers how your product is helping them achieve their goals. This might involve personalized reports, case studies, or ROI calculators.
Account Reviews: Conduct periodic reviews with customers to ensure they're getting the most out of your product and to identify any potential issues.
Feedback Implementation: Actively seek and implement customer feedback to show that you value their input and are committed to improving their experience.
Example: Adobe's Creative Cloud suite uses a multi-faceted approach to retention. They regularly update their software with new features, provide a wealth of tutorials and resources for users to improve their skills, and offer a comprehensive loyalty program called Adobe Stock.
This program allows users to earn credits for purchasing Adobe Stock content, which can be used for future purchases. By continuously providing value through product improvements, educational resources, and loyalty rewards, Adobe keeps customers engaged and loyal.
Strategies for Lifecycle Marketing Success
Now that we've outlined the stages, let's delve deeper into some key strategies that can make a real difference in your lifecycle marketing efforts.
Personalization: Tailoring the Experience
In today's market, personalization is not just a nice-to-have – it's an expectation. Here's how to make it work for you:
Segmentation: Group your users based on behavior, needs, or lifecycle stage to deliver more relevant experiences. For example, you might segment users by industry, company size, or feature usage.
Customized Messaging: Tailor your communications to address specific user segments and their unique challenges. This could involve personalized email campaigns, targeted in-app messages, or customized content recommendations.
Adaptive Product Experiences: Use data to adjust the product interface or features based on user preferences and behavior. This might include customizable dashboards or AI-driven feature recommendations.
Behavioral Triggers: Set up automated messages or actions based on specific user behaviors, such as reaching a usage milestone or not logging in for a certain period.
Upselling and Cross-Selling: Expanding Customer Value
When done right, upselling and cross-selling can significantly increase customer lifetime value while providing additional benefits to users. Consider these approaches:
Usage-Based Recommendations: Suggest upgrades or additional features based on how customers are currently using your product. For example, if a user is consistently hitting usage limits, you might recommend upgrading to a higher tier.
Complementary Services: Offer additional products or services that enhance the value of the core offering. This could include premium support packages, training services, or integrations with other tools.
Tiered Pricing Strategies: Create multiple product tiers that encourage users to upgrade as their needs grow. Ensure each tier offers clear additional value to justify the price increase.
Time-Limited Offers: Provide special upgrade offers at strategic times, such as when a user achieves a certain milestone or at the end of their billing cycle.
Example: HubSpot excels at expanding customer relationships. They offer a free CRM tool that introduces users to their ecosystem. As businesses grow and their needs become more complex, HubSpot provides clear upgrade paths to their more advanced Marketing, Sales, and Service Hubs. They also offer bundled pricing for multiple hubs, encouraging users to adopt more of their products.
Leveraging Customer Feedback
Your customers' voices are a goldmine of insights. Here's how to make the most of customer feedback:
Regular Surveys: Conduct periodic surveys to gauge satisfaction and identify areas for improvement. This could include NPS surveys, feature satisfaction surveys, or in-depth user research studies.
In-App Feedback Mechanisms: Make it easy for users to share thoughts and suggestions within the product itself. This might involve feedback buttons, feature request forms, or quick polls.
Closed Feedback Loops: Show customers how their feedback is being used to improve the product. This could involve update notifications highlighting implemented suggestions or personalized follow-ups on submitted feedback.
User Testing: Involve customers in beta testing new features or products to gather early feedback and create a sense of involvement.
Implementing Effective Referral Programs

Word-of-mouth remains one of the most powerful marketing tools. A well-designed referral program can turn your satisfied customers into a powerful acquisition channel. Key elements include:
Clear Incentives: Offer rewards that are valuable to both the referrer and the new customer. This could be account credits, extended trials, or access to premium features.
Simple Process: Make it easy for customers to refer others with minimal effort. This might involve shareable links, pre-written email templates, or in-app referral tools.
Tracking and Optimization: Monitor the performance of your referral program and refine it over time. Look at metrics like referral conversion rates, the lifetime value of referred customers, and overall program ROI.
Tiered Rewards: Consider offering increasing rewards for customers who make multiple successful referrals.
Social Sharing: Enable and encourage customers to share their referral links on social media platforms.
Example: Salesforce has built a strong community of advocates through its Trailblazer Community program. This program provides learning resources, certifications, and networking opportunities for Salesforce users. Trailblazers earn badges for their skills and can showcase these on their profiles, creating a sense of achievement and encouraging advocacy for the platform.
Conclusion
By examining these real-world examples, we can see how successful SaaS companies apply lifecycle marketing principles to grow their user base, keep customers engaged, and foster long-term loyalty. As you develop your own lifecycle marketing strategy, consider how you can adapt these approaches to fit your unique product and customer base.
Remember, the key to successful lifecycle marketing lies in continuously adapting to your customers' needs and the evolving technological landscape. Stay curious, keep experimenting, and always put your customers at the center of your strategies. With these principles in mind, you'll be well-equipped to drive growth, increase customer loyalty, and achieve lasting success in the dynamic world of SaaS.




